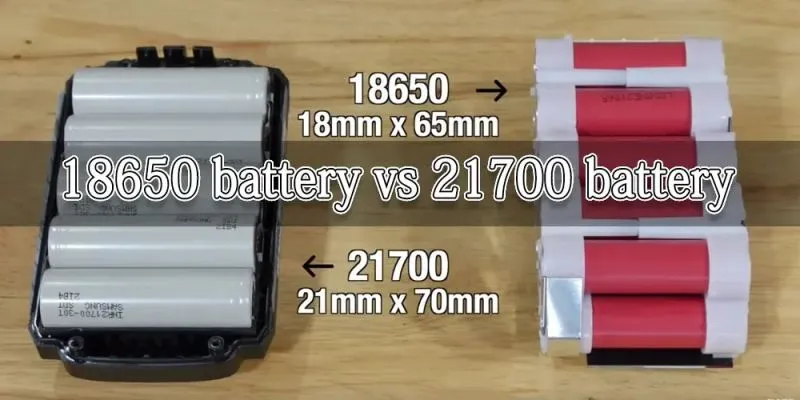
Sind 21700-Batterien besser als 18650?
Mit der kontinuierlichen Verbesserung der Batterietechnologie sind 21700 Lithium-Ionen Batterien als neuer Akteur aufgetaucht, was viele Vergleiche mit der bewährten 18650-Batterie ausgelöst hat. Also wenn

Mit der kontinuierlichen Verbesserung der Batterietechnologie sind 21700 Lithium-Ionen Batterien als neuer Akteur aufgetaucht, was viele Vergleiche mit der bewährten 18650-Batterie ausgelöst hat. Also wenn

In der Welt der Lithium-Ionen Batterien tauchen die Modelle 21700 und 18650 häufig im Gespräch auf. Beide sind zylindrische wiederaufladbare Batterien, die verschiedene Geräte mit Strom versorgen. Aber

Sind 18650 Batterien wiederaufladbar? Das ist eine häufig gestellte Frage für jeden, der Geräte verwendet, die 18650 Lithium-Ionen Zellen nutzen. Die kurze Antwort ist ja – 18650

Lithium-Ionen 18650 Batterien und alkalische AA-Batterien haben sehr unterschiedliche Eigenschaften, wenn es um Spannung, Kapazität, Größe, Anwendungen und mehr geht. Dieser Artikel bietet eine

Lithium-Ionen 18650-Akkus sind in den letzten Jahren zu einer äußerst beliebten Energiequelle für alles Mögliche geworden, von Taschenlampen und Vapes bis hin zu Elektrowerkzeugen und sogar Elektrofahrzeugen. Aber um

18650-Akkus sind in den letzten Jahren enorm populär geworden. Man findet diese Lithium-Ionen-Zellen, die Vapes, Taschenlampen, Elektrowerkzeuge und sogar Elektrofahrzeuge antreiben.

Lithium-Ionen 18650-Akkus sind in den letzten Jahren äußerst beliebt geworden. Da immer mehr Geräte 18650-Akkus als Energiequelle verwenden, ist es wichtig zu lernen, wie man sie richtig auflädt
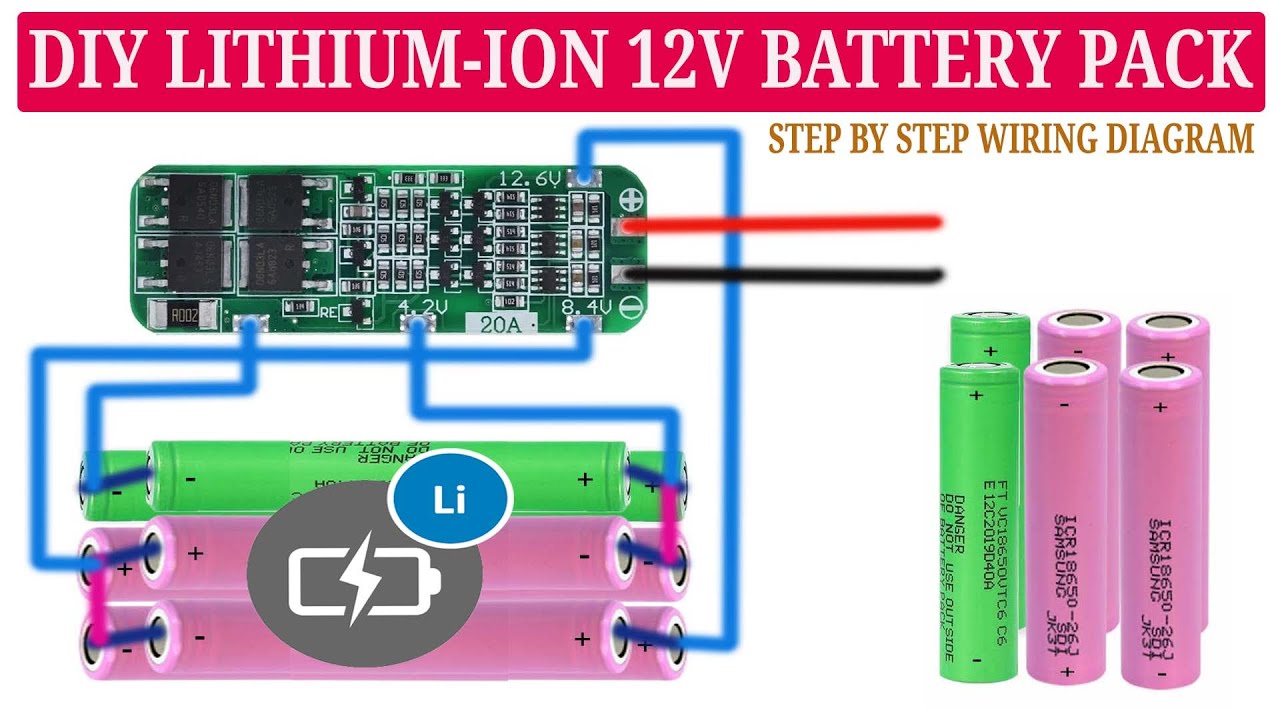
Eigene maßgeschneiderte 12V 18650-Lithium-Ionen-Akkupacks herzustellen, klingt vielleicht einschüchternd. Aber ich werde Sie durch den gesamten Prozess führen, Schritt für Schritt. Egal ob Sie

Das eigene 18650-Akkupack herzustellen, mag einschüchternd erscheinen, ist aber tatsächlich ein unkompliziertes DIY-Projekt, wenn man die richtigen Teile, Werkzeuge und Kenntnisse hat.

Wir alle sind im Alltag auf elektronische Geräte angewiesen, und viele dieser Geräte werden von wiederaufladbaren Lithium-Ionen-Akkus betrieben. Einer der beliebten
Nuranu wurde 2012 gegründet und ist ein Hightech-Unternehmen, das sich auf die Entwicklung, Herstellung, Vermarktung und den Service von wiederaufladbaren Akkuprodukten und Zubehör spezialisiert hat.

