LFP(Lithium) battery Vs NMC battery: difference and which is better
LFP(Lithium) battery Vs NMC battery: The world of battery technology is ever-evolving, and it can be challenging to keep up with the changes. Lithium Ferro Phosphate (LFP) and Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) are two popular batteries. This article will explore the differences between these two types of batteries and provide a comprehensive comparison to help you decide which is best for your needs.

What is an NMC battery?
An NMC battery is a lithium-ion battery composed of a cathode combination of nickel, manganese, and cobalt. This type of battery is known to provide more watt-hours of capacity than Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP). NMC batteries can be used in various applications, including consumer electronics and electric vehicles. They provide a longer life cycle than other batteries and can be recharged quickly and safely. NMC batteries are becoming increasingly popular due to their high performance and reliability.

What is LFP?
A Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) battery is a lithium-ion battery used in various applications. It is composed of lithium iron phosphate, an environmentally friendly compound. These batteries can charge and discharge at high speeds, making them ideal for applications requiring a lot of power. Due to their chemistry, they are also more stable and safer than other lithium batteries. This makes them an attractive option for electric vehicles, solar energy storage, and consumer electronics applications. LFP batteries offer many advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries, making them an attractive option for various applications.
LFP Vs NMC: What are the difference?
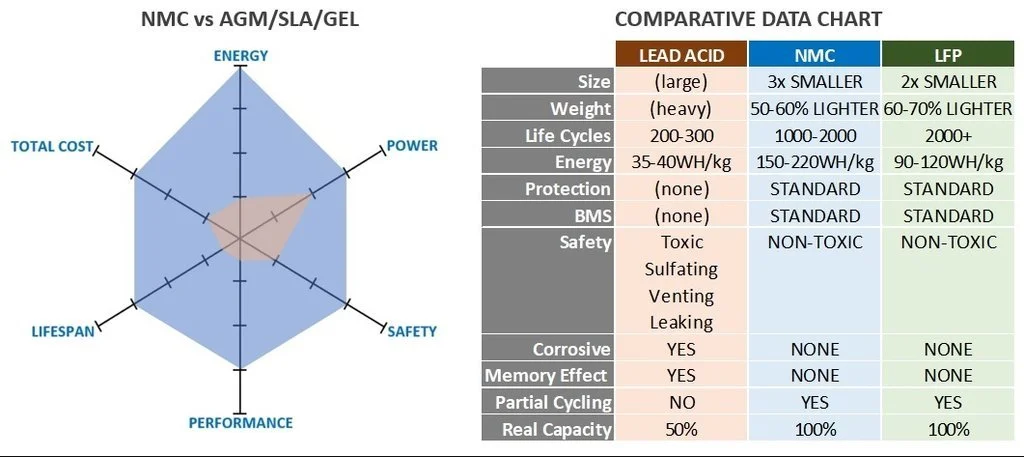
LFP batteries and NMC batteries are two types of lithium-ion batteries that use different cathode materials. LFP batteries use lithium phosphate, while NMC batteries use lithium, manganese, and cobalt. Compared to NMCs, LFPs are more efficient and perform better when the state of charge is low, but NMCs can endure colder temperatures. However, LFP batteries hit thermal runaway at a much higher temperature than NMC batteries, reaching 518° F (270° C) versus 410° F (210° C). NMC batteries tend to be slightly cheaper than LFP batteries due to their economies of scale. The choice of battery type depends on the application and the user’s needs.
LFP Vs NMC: Price
LFP batteries are known for their high energy density, no thermal runaway, low self-discharge, and superior charging performance in cold temperatures. At the same time, the initial CAPEX of LFP batteries is usually priced more competitively than NMCS. NMC batteries have more watt-hours of capacity when the same mass is used. As such, NMC batteries may be a better choice when the range is a priority, as LFP batteries still need to match the range of higher nickel NMCs.
LFP Vs NMC: Energy density
LFP batteries have a lower energy density than NMC batteries, but they still perform well. The cathode material in LFP batteries is Lithium Iron Phosphate, which gives them moderately to extended life span and good acceleration performance. However, NMC batteries have an even higher energy density, around 100-150 Wh/Kg. They reach thermal runaway at 410° F (210° C), while LFP batteries get there at 518° F (270° C). Despite the lower energy density, LFP batteries are superior to NMC batteries in energy storage.
LFP Vs NMC: Temperature tolerance
LFPs have suffered from poor charging performance at shallow temperatures. On the other hand, NMC batteries have a relatively balanced temperature tolerance. They can generally work in average low and high temperatures but hit thermal runaway at 410° F (210° C). More than 100° F lower than LFP batteries, which hit thermal runaway at 518° F (270° C). That is to say, LFP batteries have better high-temperature resistance than NMC batteries
LFP Vs NMC: Security
Regarding safety, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries are generally superior to Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC) batteries. This is because LFP cells have a unique combination of lithium iron phosphate, which is more stable than nickel and cobalt-based cathodes. Additionally, LFP batteries have a much higher thermal runaway temperature of 518° F (270° C) compared to NMC batteries which reach 410° F (210° C). Both battery types utilize graphite. However, LFP batteries are better in energy density and self-discharge. All in all, LFP batteries are the go-to choice for secure and reliable power sources.
LFP Vs NMC: Cycle time
Regarding cycle time, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries have a much longer life than Nickel Metal Hydride (NMC) batteries. Typically, the cycle life of an NMC battery is only about 800 times, whereas, for LFP batteries, it is more than 3000 times. Moreover, with opportunity charging, the useful life of both battery chemistries can range from 3000 to 5000 cycles; therefore, if a user needs a battery with long cycle life. LFP batteries are the better choice as they can provide full power for more than three years before they start to degrade.
LFP Vs NMC: Service life
When it comes to service life, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries have a clear advantage over Nickel-Metal Hydride (NMC) batteries. LFP batteries often come with a six-year warranty; their expected lifetime is at least 3000 cycles(possibly more than ten years of use). On the other hand, NMC batteries usually only last for around 800 cycles and must be replaced every two to three years. LFP batteries offer a much longer service life than NMC batteries.

LFP Vs NMC: Performance
Regarding performance, LFP batteries are superior to NMC batteries for several reasons, including their higher energy density. This higher energy density means better acceleration performance and improved energy storage. However, one potential downside of LFPs is their lower charging performance at shallow temperatures. NMC batteries tend to be cheaper than LFP ones due to their economies of scale and their use of lithium, manganese, and cobalt oxide as the cathode material. Ultimately, the choice between an LFP and an NMC battery will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the user.
LFP Vs NMC: Value
When it comes to value, the choice between a Lithium Ferro Phosphate (LFP) battery and a Nickel Metal Hydride (NMC) battery depends on your needs. LFP batteries are typically more expensive than NMC batteries. Still, they offer some advantages that make them worth the extra cost.
The main advantage of an LFP battery is its superior longevity. It can last up to twice as long as an NMC battery, making it an excellent choice for applications that need reliable power over a long period. LFP batteries have better temperature tolerance than NMC batteries, so they are better suited for extreme climates.
On the other hand, if you’re looking for a more economical option, an NMC battery may be the right choice for you. They are cheaper than LFP batteries and still perform well in most applications. Ultimately, the best value depends on your specific needs and budget.
Which battery wins
When it comes to Lithium-ion batteries, there is no clear winner between Lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) and Nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC). Each battery has its advantages and best-suited scenarios. LFP batteries are known for their superior safety features, higher energy density, no thermal runaway, and low self-discharge. Meanwhile, NMC batteries offer a slightly lower cost due to economies of scale and require less space. Ultimately, the choice of battery will depend on the application and the consumer’s specific needs.
LFP Vs NMC: How to choose to right one for you?
When deciding between an LFP and NMC battery, it is essential to consider its intended use. Suppose you need a battery for a long-term application such as solar energy storage. In that case, an LFP battery is likely the best choice due to its longevity and durability. On the other hand, if you need a battery for a short-term application such as powering an RV or boat. Then an NMC battery may be more suitable due to its higher power output and faster charging capabilities.
In addition to considering your intended application, you should also consider factors such as cost and safety. LFP batteries are typically more expensive than NMC batteries. Still, they offer better safety features and can last up to 10 times longer than NMC batteries. On the other hand, NMC batteries are generally cheaper but require more frequent maintenance and have less reliable safety features.
Choosing between an LFP and NMC battery depends on your individual needs and budget.

Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) battery and the Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) battery have advantages and disadvantages. The NMC battery is the best choice if you are pursuing high performance. Still, if you’re looking for longevity and safety, LFP batteries are your better choice.
When selecting between these batteries, it is essential to weigh various factors, including safety, performance, cost, and capacity. Both types of batteries can be suitable for multiple applications, depending on which features are essential for your specific needs.








